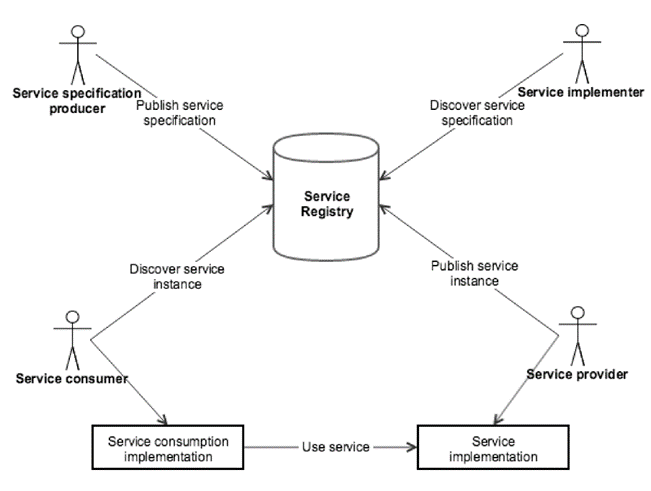
Within the realm of e-Navigation, a Maritime Service in the context of e-Navigation can be implemented by one or more e-Navigation Technical Services. Drawing inspiration from service-oriented architectures, a Technical Service is defined as a cohesive set of software functions that can be repurposed for various needs, along with the policies that oversee and regulate its application.
In essence, a Technical Service is a digital service offered by an electronic device to another electronic device.
This page aims to improve the visibility and accessibility of available e-Navigation Technical Services and information provided by them. This enables service providers, consumers, and regulatory authorities to share a common understanding of a Technical Service and how to implement and use it.
Service specifications
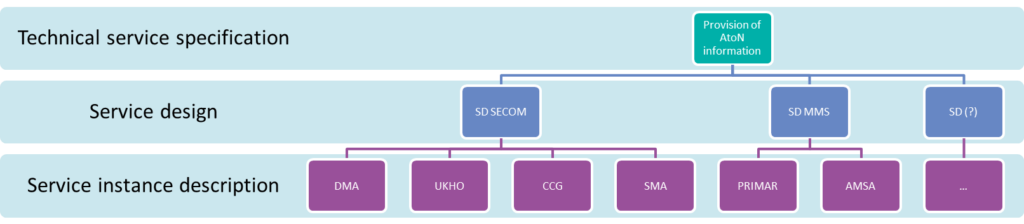
Service specifications play a crucial role in achieving the outcomes of service identification and design processes. They serve to chronicle the pivotal features of a specific service at the logical tier. The service specification provides a holistic overview of a service and its building blocks at the logical level.
The service specification is intended to be technology-agnostic. The service specification shall not describe the details of a specific service implementation. For that purpose, a service design description shall also be provided, where the actual realisation of the service with a dedicated technology shall be described.
List of Technical services available Link download:
| Service Specification | IALA Committee | Referenced Data Models | Completion Date | Service Design | Service Design Completion Date |
| Marine Aids to Navigation (AtoN) Technical Service Specification for the provision of AtoN information | ARM, DTEC | S-125 | Version 1.0: ARM18 Version 2.0: (depending on S-125) | SECOM based | Version 1.0: ARM19 |
| Marine Aids to Navigation (AtoN) Technical Service Specification for the provision of enhanced AtoN information | ARM, DTEC | S-201 | SECOM based | ||
| Voyage information service | VTS, DTEC | S-421, … | |||
| Route exchange service | VTS, DTEC | S-421, … | Edition1.0.0:VTS57 | Route exchange Ed1.0.0: VTS57 | |
| S-200 based ASM provision | DTEC | S-230 | |||
| Slot management service | VTS, DTEC | ||||
| Traffic clearance service | VTS, DTEC | S-212, S-421 | Edition 1.5: VTS 57 | SECOM based | Edition 1.2.0: VTS 57 |
| Anchorage assignment service | VTS, DTEC |
Disclaimer for Test versions (Below version 2.0.0)
This document pertains to Test Versions of the Product Specifications. Please be advised that this version is intended solely for testing and evaluation purposes and is not prepared or suitable for actual implementation. Any unexpected outcomes or issues arising from the use of this test version are not the responsibility of IALA or any affiliated entities.
Users should exercise caution and discretion when using the test versions, keeping in mind its limitations and the purpose for which it is designed. It is important to note that Version 2.0.0, when released, will be fully equipped and intended for actual implementation. Users are encouraged to wait for Version 2.0.0 for any operational or implementation purposes.
By using the Test versions, users acknowledge and agree to this disclaimer and its terms.
Service design
The service design description equips service architects and designers with a systematic, documented portrayal of the service’s technical layout. Guideline G1128 offers a template detailing the layout of sections the author should complete during the service technical design phase.
Service instances description
The service instance description’s core objective is to catalog, in an easily comprehensible format, all information pertinent to a particular service’s implementation and instantiation.
Note that one service implementation may be deployed several times at different access points thus forming several different service instances. In this case, several service instance description XML files need to be produced – one for each deployed instance, whereas the service instance description document can be identical if all instances behave equivalently.
Related documents
Service specifications
Service design
