Angle of Divergence
2-1-100
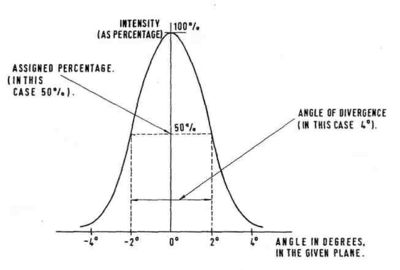
The angle formed by two rays of a luminous beam in a given plane, the intensity within the angle being at least equal to an assigned percentage of the maximum of the curve of the intensity distribution in that plane.
Most often the plane is either vertical (vertical divergence) or horizontal (horizontal divergence).
The value of the assigned percentage has differed widely, the most common values being 10%, 15% or 50%.
For an optical apparatus which does not produce a converged beam (2-2-215) or a diverged beam (2-2-220), the angle of divergence is also defined approximately by radians or degrees, where f is the focal distance of an optical apparatus and d is the maximum dimension of a light source placed at its focus, measured in the same plane as the angle of divergence.
Note: The word Divergence is also used as an abbreviation for "angle of divergence".
Please note that this is the term as it stands in the original IALA Dictionary edition (1970-1989)